The diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis is made on the basis of simple studies - X-rays. In order for the disease to recede, an integrated approach to the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is needed.
In order for the disease to recede, an integrated approach to the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is needed.
Why does cervical osteochondrosis occur?
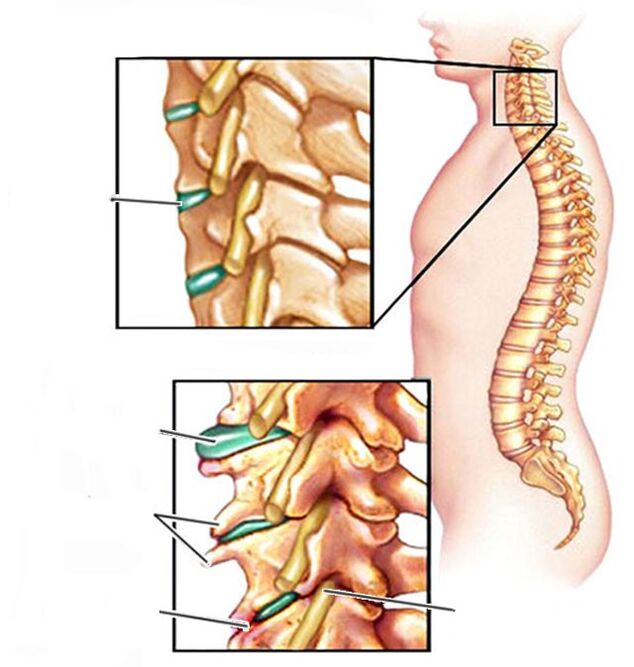
The pain has several foci of localization: neck, head, shoulders. Weakened neck muscles provoke the development of osteochondrosis. Due to improper posture, inactivity and the adoption of unnatural postures, some neck muscles are constantly tense, others spend too much time at rest. The spine adapts to an irrational load at the cost of its health. The following changes are noted in cervical osteochondrosis:
- violation of blood and lymph flow;
- lack of nutrition of the connective tissue of the intervertebral discs;
- instability of the position of the vertebral bodies towards each other.
The structures of the vertebrae and discs are gradually being destroyed. This process is irreversible, so you need to take care of your health in time and immediately undergo treatment for the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, without delay for later. Reasons also include:
- neck injuries;
- extra pounds;
- connective tissue dysplasia;
- poor nutrition, insufficient water intake.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine: symptoms
Main signs (vertebrae):
- Pain. It can be a constant withdrawal or appear during the period after the static position of the neck, sleeping in an uncomfortable position. There are sharp pains that briefly immobilize the patient (lumbago);
- Torticollis or difficulty moving. Sometimes it is so painful to turn or tilt the head that the person finds a comfortable position where the pain is minimal and tries to stay in it;
- Muscle tension, feeling of stiffness, heaviness;
- Crunching of the vertebrae when turning the head. Extravertebral symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis (involving nerves and surrounding tissues);
- Muscle inflammation;
- Headache, migraine, dizziness, sometimes with nausea and vomiting;
- Occipital pain, increased intracranial pressure, feeling of heavy head; such symptoms sometimes occur so clearly that the term "osteochondrosis of the head" has taken root among patients. It is obvious that headache is only a secondary manifestation of pathological changes in the skeletal system, and it is correct to speak of cervical, not osteochondrosis of the head;
- Sensory disorders: hearing and vision impairment, speech, ringing in the ears due to lack of food in the brain;
- Pain in collarbone, hands lowered to palms;
- Tingling and chills in the neck and arms, sometimes numbness in the fingers;
- Limiting the range of motion of the arms (possible on one side).
Dangerous consequences of cervical osteochondrosis: treatment is mandatory!
If the degenerative changes do not stop, osteochondrosis can be added:
- radicular pain due to constriction of nerves arising from the spine;
- protrusions and hernias, which compress the spinal cord and lead to complete paralysis;
- cervicocranialgia (cervical migraine, dystonic stage of vertebral artery syndrome);
- formation of osteophytes on the vertebrae.
Methods for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis of the spine
It is impossible to cure this disease with drugs. You can only eliminate the pain syndrome with analgesics. But they always have side effects, so it is advisable to use them only in extreme cases. The symptoms and treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine vary from patient to patient and require an individual approach.
Doctors have at their disposal a rich arsenal of advanced technologies, which can select the most efficient and effective. Effective in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis and its manifestations:
- traction on the DRX robot - restores the correct position of the vertebrae without the risk of injury;
- shock wave therapy - improves blood and lymph flow to the affected area, restores metabolic processes, relaxes muscles;
- interstitial electrical stimulation - fights the complications of osteochondrosis, relieves pain caused by inflammation of the pinched nerve;
- HILT - laser therapy that currently relieves pain.
The next stage in the treatment of the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis is to restore the blood supply, strengthening the proper position of the vertebrae. Rehabilitation can last several sessions and includes physiotherapy, manual therapy and the use of modern devices. The more accurately the patient follows the recommendations of experts, the greater the efficiency of the techniques. The final phase is in the patient's area of responsibility:
- lifestyle and diet correction;
- regular exercise therapy;
- active life position and optimism.























