Pain in the shoulder blade and below can occur with nerve damage, spinal disease, shoulder girdle or somatic pathologies. The cause can be determined by clinical signs, conditions for the manifestation of the syndrome and anamnesis data.
Pain in the area of the shoulder blade can be felt during inhalation, felt in half of the body and or in the whole arm. In certain cases, such symptoms are the "first bell" of the exacerbation period, which can be prevented after the provoking factor is established.
Causes and localization
Pain under the shoulder blade usually occurs during movement - it is preceded by an awkward turn, long standing with a bent back. It signals local damage that occurs for a variety of reasons.
Pathologies with unilateral lesions, in which pain is only on the right or left side below the shoulder blade, are rare - usually the severity of symptoms is individual. This is due to the symmetrical arrangement of the nerve roots that extend from the spinal cord.
Injuries
If there is pain under the right and left shoulder blades, it may be due to damage to the bones and muscular frame. Symptoms do not have a strict localization, the severity depends on the traumatic factor. The clinic is usually acute, begins abruptly and takes a chronic course.
The causes of traumatic pain under the left or right shoulder blade are as follows:
- Bruises - in such cases the pain is superficial, the muscles are most often damaged. Usually the back muscles under the shoulders and under them hurt, swelling and local inflammation develop. After 2-3 weeks, the symptoms disappear.
- Cracks and fractures are more serious injuries, the pain is concentrated in the shoulder blade itself. At the slightest movement it intensifies, the patient cannot move his arm or bend.
- Subluxation and displacement of the vertebrae - this leads to pain in the joints at the level of the shoulder blades and below, sometimes the bone structures compress the nerve roots.
Injuries are characterized by severe pain below the right or left shoulder blade, which occurs spontaneously. Creaking and squeaking may occur during movement.
Osteochondrosis
If the disease affects the thoracic spine, the patient has back pain near the shoulder blades and below. This is due to pinching of nerves or spinal cord due to deformation of the articular disc. The pathology develops gradually, and as the distance between the vertebrae decreases, the clinic of pathology worsens.
The location of the pain depends on the affected area:
- If osteochondrosis destroys the articular discs of the thoracic region from 2 to 6, pain in the shoulder blade is felt. It usually radiates to the neck and arm. When the veins constrict, dizziness occurs, intracranial pressure may increase.
- When joints of 6-12 segments are affected, the pain radiates below the left or right shoulder blade, spreading lower, to the corresponding half of the body and lower back.
The spinal roots of the thoracic region create plexuses that innervate the arms and torso. Therefore, when compressed, the pain spreads along their course.
In osteochondrosis, the discomfort is one-sided - pain in the shoulder blade on the right or left side and below, depending on the skew of the spine.
Scoliosis
This is the curvature of the spine in the transverse direction due to the overstrain of the muscles that support posture. This leads to pinching of the roots and spinal cord, the appearance of pain under the shoulder blade on the right or left side. Pathology is usually accompanied by:
- Respiratory insufficiency - unilateral skew of the spine deforms the chest, which affects the functioning of the lungs, one of which is compressed, and the other takes over the lost function.
- Cardiac disorders - the frequency of contractions and changes in heart rate, shortness of breath and pale skin.
- The appearance of visible deformity of the chest is the main cause of pain under the right or left shoulder blade. The vertebrae, together with the ribs, are displaced laterally, which causes them to move downwards on the side of the curvature of the bone structure and damage the spinal cord with their branches.
If the spinal cord is compressed during scoliosis, the back usually hurts between the shoulder blades and below, the focus is strictly limited. If muscle spasms coalesce, the symptom spreads to adjacent structures.
Kyphosis
It is characterized by bending the spine backwards, moving the shoulder girdle forward, and gradually bending. There is pain over the shoulder blade - usually on both sides, giving in the arm and neck. The following mechanisms participate in its formation:
- Neurogenic - due to the curvature, the distances between the vertebral bodies in the front parts are reduced, which causes pinching of the spinal cord branches. There is pain in the right and left shoulder blades, which can spread to the collarbone, neck and shoulder.
- Muscular - deviation of the spinal column leads to overexertion of the muscles of the neck zone, which can painfully spasm in the area of the shoulder blades and below.
As a result of kyphosis, the vertebral artery is compressed, the cerebral circulation is disturbed. The work of internal organs is gradually deteriorating.
Spondylarthrosis
If the right or left shoulder blade hurts, one of the reasons may be spondylarthrosis - damage to the facet joints and intervertebral discs. It is followed by loss of mobility, stiffness appears, most pronounced in the morning.
The clinical picture changes as the pathology progresses: >
- Destruction of cartilage - with a lack of blood circulation, the integrity of the connective tissue is disturbed, the articular disc becomes fragile, more damaged and recovers more slowly. At this stage, strong physical exertion leads to microtrauma, there is pain radiating to the shoulder blades and below.
- Deformation of the articular disc - seals appear that interfere with mobility. This causes new destruction, which slows down the regeneration processes, the patient feels pain in the back and shoulders.
- The appearance of bone growths is characteristic of the advanced stage of the disease. Neoplasms damage joints, muscles, blood vessels and nerves.
In spondyloarthritis, the back can ache between the shoulder blades or below - the attack is usually preceded by physical activity. At rest, the symptoms subside, because the bone growths do not damage the surrounding tissues.
Protrusions and hernias
In these conditions, acute pain under the left and right shoulder blade, which occurs due to compression of the spinal cord or its roots, is worrying. As a result of pinching, sensitivity along nerve fibers is impaired.
The localization of symptoms is as follows:
- Pain in the shoulder blades and above - protrusion or hernia in the cervicothoracic region or when 1-3 thoracic segments are affected. The symptom intensifies when you try to tilt your head, turn it to the side.
- Pain in the interscapular region - in this case the middle parts can be affected, from 3 to 6. The discomfort increases when both hands move to the side, take a deep breath or turn.
- Severe pain under the right and left shoulder blades - articular discs 6 to 12 are affected, lower back may be involved in pathology. In this case, there is a risk of developing a hernia, because this part of the spine is more stressed than before.
Unlike spondyloarthritis, the pain of hernia and protrusion does not last long at rest. This is due to constant nerve compression, which is exacerbated by muscle cramps.
Radiculitis
This is a pinching of the lumbar roots, which are gathered in a strong sciatic nerve. If its upper parts are affected, the patient feels pain under the shoulder blade and under it, on both sides, intensified by flexion and sudden movements.
As the disease progresses, additional symptoms may occur: >
- There is pain in the back that radiates to the lower extremity - a sharp stabbing pain is felt as an electric shock along the nerve flow.
- Burning pains in the back, in the lumbar region or under the shoulder blades indicate prolonged pinching of the spinal roots in the lumbar region.
- Cramps and loss of sensation most often occur in the lumbar region, buttocks, sometimes numbness along the nerve fibers on the thigh, lower leg and foot.
Shoulder-scapular periarthrosis
This condition is an inflammation of the shoulder joint and surrounding tissues, there is stiffness that disappears only after warming up.
The pain is concentrated in the area of the right or left shoulder blade and below, depending on the development of hemispheric motor skills (right-handed or left-handed). It appears first after exercise and then at rest. Additional symptoms occur along the way:
- headache;
- numbness of the hands;
- violation of spinal mobility.
In humeroscapular periarthrosis, the clinical manifestations increase when the arm is raised - pain in the right or left shoulder, shoulder blade. Gradually, the range of motion decreases, the stiffness progresses.
Neuralgia
Another cause of pain under the right or left shoulder blade is inflammation of the nerves in this area. The disease is caused by hypothermia, draft. Most commonly affected:
- Suprascapular and supraspinous nerves - pain occurs in the right or left shoulder blade from the back, concentrated mainly in the collarbone. Sometimes the discomfort spreads to the shoulder, which indicates the defeat of the skin branches of this area.
- Subscapular and infraspinatus nerves - in this case pain on the right or left side under the shoulder blade, depending on the side of the lesion. If the muscles of the same name are affected, the clinical manifestations worsen when the arms are moved down, abducted behind the back.
- Intercostal nerves - usually 1-4 pairs. These branches go along the lower edge of the ribs, the pain occurs not only in the area of the shoulder blades and below, but also on the sides of the chest, sometimes in the front parts.
Symmetry is not typical of neuralgia - if the left half of the body has been exposed to drafts, then pain in the neck, chest and shoulder blades is noticed on this side.
Heart disease
The branches of the parasympathetic tree, which is connected to the spinal cord and its roots, go to the heart. Therefore, heart disease can cause pain in the shoulder blade and below. Usually, a mild form of myocardial infarction is latent. It may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Dull pressing or burning pain that is felt behind the sternum or under the left shoulder blade - can last for hours, intensifies when walking, but disappears a little at rest.
- Shortness of breath - accompanied by pain, may manifest within a few days.
- Tachycardia - increased heart rate, sometimes arrhythmias.
- Other symptoms include high blood pressure, dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
Gastrointestinal problems
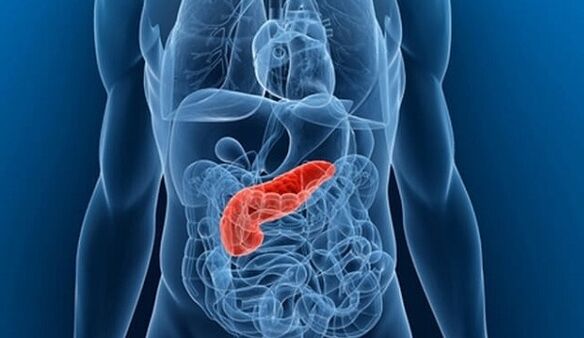
Similar to the previous mechanism, the pain spreads along nerve fibers. Clinical signs can be bilateral, but in most cases there is a certain pattern in which symptoms appear according to the location of internal organs.
Pain under the left shoulder blade from the back occurs in the following diseases:
- pancreatitis;
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer.
Usually, patients with these diseases complain of dyspeptic disorders, nausea and vomiting. If internal bleeding occurs, pale skin, dark stool color, decreased pressure and weakness are noticed.
Pain under the right shoulder blade from the back follows:
- cholelithiasis;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum.
Other reasons
In addition to these factors, pain under the shoulder blades can cause:
- Uncomfortable mattress - if it breaks and you sleep on the right side, in the morning you can feel pain under the left shoulder blade from the back, because the curved spine pinches the spinal roots.
- Pleuritis - pain in the scapular region occurs when breathing due to the friction of the leaves against each other, culminates in deep breathing.
- Poliomyelitis - the pathology is accompanied by neurological symptoms, back pain often occurs.
- Intoxication - severe poisoning or cold can be manifested by muscle pain, chills and fever.
- VVD - vegetovascular dystonia is accompanied by changes in pressure, interruptions in the work of the heart and shortness of breath, and sometimes discomfort in the back.
- Kidney disease - such pathologies are characterized by aching or stabbing pain under the right shoulder blade, changes in diuresis and urine color, and general symptoms.
- Subdiaphragmatic abscess - if suppuration is observed in the upper floor of the abdominal cavity, pain under the shoulder blades, fever and symptoms of intoxication will be felt when inhaling.
- Mental disorders - In some cases, pain in the shoulder blades and below them can be the result of such disorders. The exact mechanism of occurrence has not been studied.
The nature of pain
Pain in the area of the shoulder blades and below can be different, by its nature it is possible to assume a certain group of pathologies, sometimes a provoking factor can be established:
- Clamped nerves are characterized by lumbago - a sharp stabbing pain that occurs with a sudden turn of the body, raising the arm. This is the main difference from cholelithiasis, in which the symptom does not twist from movement.
- Painful, pulsating or burning pain indicates pathology of internal organs. The last option occurs when squeezing the roots of the spinal cord, but it increases with movement and can turn into suturing.
- Hernia is characterized by severe squeezing pain in the shoulder blades and below. Sometimes it is preceded by lumbago, numbness of the limbs.
- Cutting of different intensity is characteristic of neuralgia, drilling often accompanies inflammation of the joints.
Which doctor treats shoulder pain?
If you feel pain in the shoulder blade and below, it is necessary to schedule an examination with a neurologist. If there are no trapped nerves, the specialist will refer you to a consultation with an orthopedist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist or urologist, depending on the suspected disease.
Diagnosis
To determine the cause of discomfort in the scapular area and below, a laboratory and instrumental examination is performed:
- X-ray or CT - with these methods you can detect osteochondrosis, curvature of the spine and the consequences of injuries.
- MRI >- the spinal column, shoulder joint or internal organs are examined, depending on the suspicion of pathology.
- ECG - helps identify heart disease.
- Blood and urine tests are informative for some somatic pathologies, inflammation of muscles and joints.
- Ultrasound - is prescribed for somatic diseases, if it is impossible to undergo MR.
Usually, pain under the shoulder blades occurs due to neurology. Therefore, CT and MRI are considered the "gold standard" in the diagnostic protocol.
General principles of treatment
The main task is to eliminate the symptoms and the provoking factor. The patient's well-being is stabilized first, then the underlying pathology is treated.
The therapy program includes:
- Medications - Analgesics are usually prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation. Then the means are prescribed depending on the underlying disease - antibiotics, gastroprotectors, diuretics.
- Physiotherapy - strengthens the spine, cures somatic diseases. Medical electrophoresis is used in the blade area, heating procedures, SWT.
- Massage - warming up is carried out with damage to the spine. These procedures relax the muscles above and below the shoulder blades, and improve posture. In that case, you need the professional help of a chiropractor or osteopath.
- Gymnastics - is carried out after the removal of pain, the program is compiled, depending on the disease suffered by a physiotherapist, rehabilitation specialist.
Prevention
After successful treatment, patients are advised to follow a preventive program that will prevent the recurrence of pathology:
- watch your posture;
- choose a mattress of moderate hardness and an orthopedic pillow;
- twice a week, massage in the area of the shoulder blades and below;
- follow a low calorie diet for obesity;
- get rid of bad habits;
- carry out prophylaxis of somatic pathology (if present in the anamnesis);
- see a doctor every six months.
Pain in and below the shoulder blades can be neurological or somatic in nature. When the nerves are damaged, the symptoms are acute and sudden, they appear spontaneously.
Pathologies of internal organs and joints are characterized by gradual and long-lasting pain, the clinic is always accompanied by additional symptoms. In the initial stages, analgesics are prescribed, and after the diagnosis, the program is supplemented with etiological therapy and strengthening procedures.























